Cambodia is currently implementing the first phase of its the Pentagonal Strategy for growth, employment, equity and efficiency, a vision for 2050. In relation to Sustainable Consumption and Production, Cambodia adopted its Environmental Code in 2023. The ENR Code has a multi-fold strategic objective, which includes ensuring development and sustainability. It provides a common strategic direction for environmental protection and conservation of natural resources to relevant ministries, institutions, and authorities. Its National Strategic Plan on Green Growth for 2013-2030focuses on leading the country towards a “green civilisation”, with special emphasis on green investment and green jobs creation, green/blue economy, natural resources management and green technology management. In 2021, Cambodia also adopted a Circular Economy Strategy and Action Plan in consultation with an inter-ministerial Technical Working Group of Sustainable Consumption and Production. This CE Strategy and Action Plan aims to (i) increase efficient use of Raw Materials (ii) promote sustainable design, production, remanufacturing and distribution and (iv) promote sustainable consumption and effective reuse and repair. The National Council for Sustainable Development (NCSD) – an inter-ministerial body, established to develop and coordinate policy on sustainable development – plays a central leadership role on the SCP agenda. A prakas on E-Waste Management was issued in March 2025; it establishes extended produced responsibility (EPR) and mandates that producers, importers, and suppliers become accountable for the collection, management, and disposal of their end-of-life products, such as electronics.
Connection to the Global Agenda
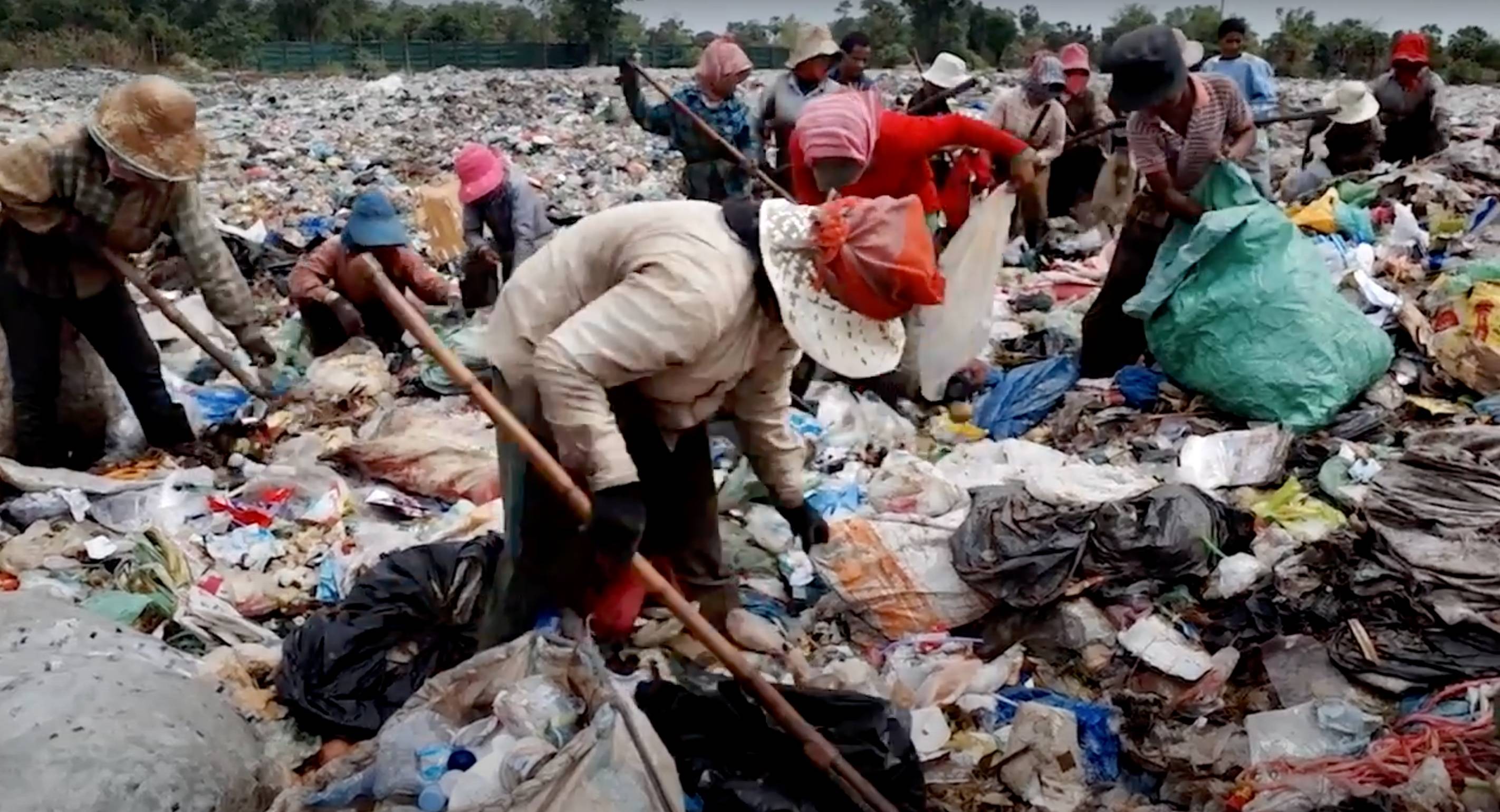
In localizing the SDGs, Cambodia has selected two out of the global SDG 12 targets (12.4 and 12.5), related to pollution, waste management and recycling. Cambodia has adopted the Stockholm Convention related to Persistent Organic Pollutants and the Minamata Convention on Mercury (target 12.4). As noted in the 2023 Voluntary National Review, in its efforts to improve waste management, the Ministry of Environment enacted the 2023 Environmental and Natural Resources Code, which provides the legal framework for managing Municipal Solid Waste, Electrical and Electronic Waste, and Plastic Bag Management (in line with target 12.5). Royal Government of Cambodia is putting in place first elements for the implementation of green public procurement (target 12.7).
A Key Solution to Climate Change
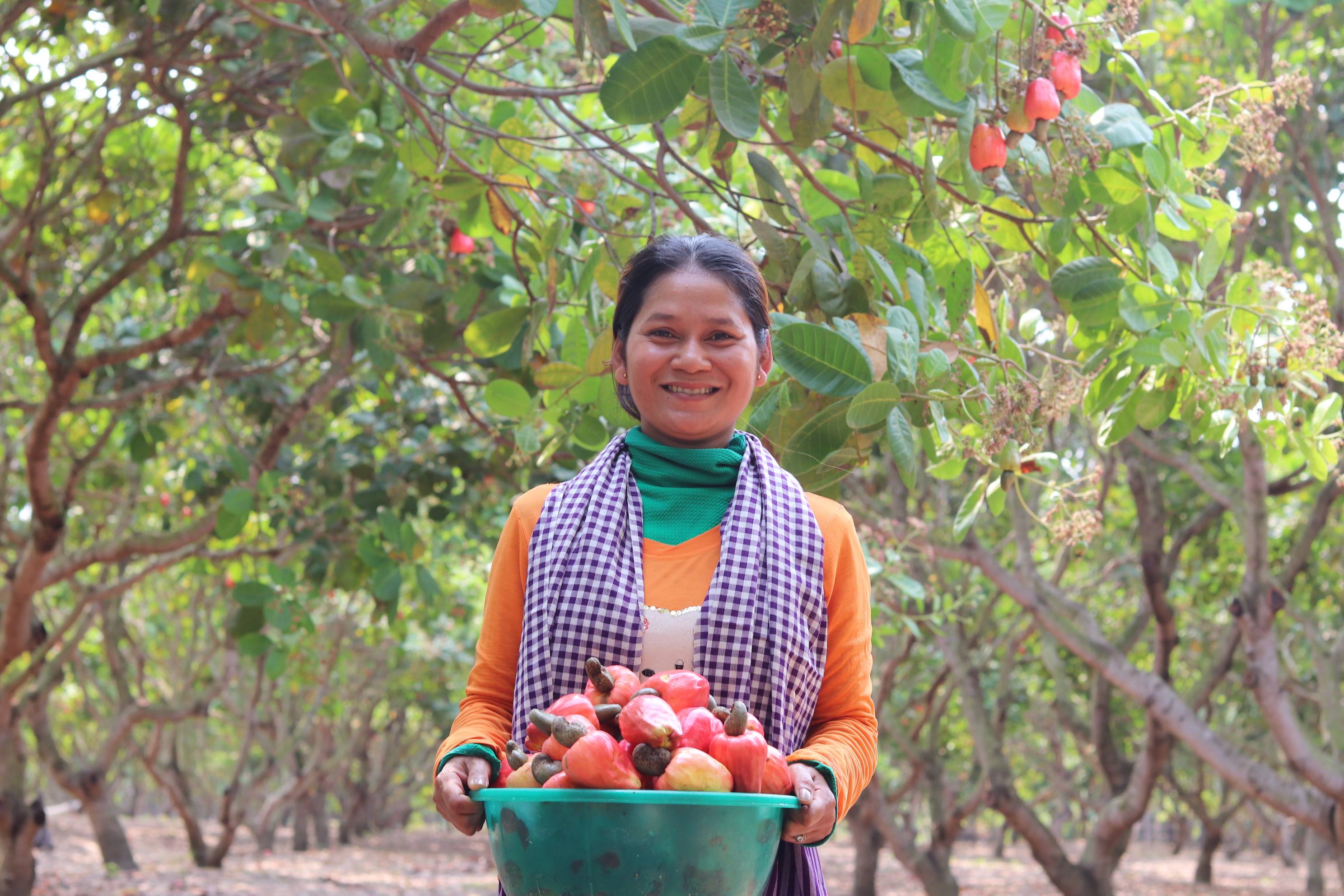
Cambodia is regularly ranked amongst the countries most vulnerable to climate change. This is due to a combination of its geography, relatively high reliance on agriculture, forestry and fisheries and low adaptive capacity resulting from the shortage of technically skilled human resources, institutional capacities and adaptation financing. Over 80% of the population live in rural areas and are overly exposed to increasing and more unpredictable floods and prolonged droughts. The Cambodian government’s response to climate change includes a Climate Change Strategic Plan (CCSP) 2024-2033 adopted in 2025, sectoral Climate Change Action Plans for each line Ministry, and the 3rd Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC3.0) to the Paris Climate Agreement submitted to UNFCCC in 2025. Cambodia’s NDC3.0 includes a total of 163 measures on mitigation, adaptation and enabling environment across five key sectors, including energy, industry, agriculture, forestry and waste. In the agricultural sector, the plan emphasizes promoting climate-smart practices, expanding the use of biodigesters for waste management, and scaling up farmer certification. The energy sector aims for a transition to renewables, with a target of 80% renewable energy by 2035, and includes initiatives for electric mobility and decentralized rural electrification. For forestry, NDC 3.0 seeks to halve the deforestation rate by 2030, aligning with the country's carbon neutrality goals. A key component involves mobilizing green finance through mechanisms such as the Cambodia Sustainable Bond Accelerator to fund these climate initiatives and ensure a transition towards a more resilient and inclusive economy.
Priority Sectors
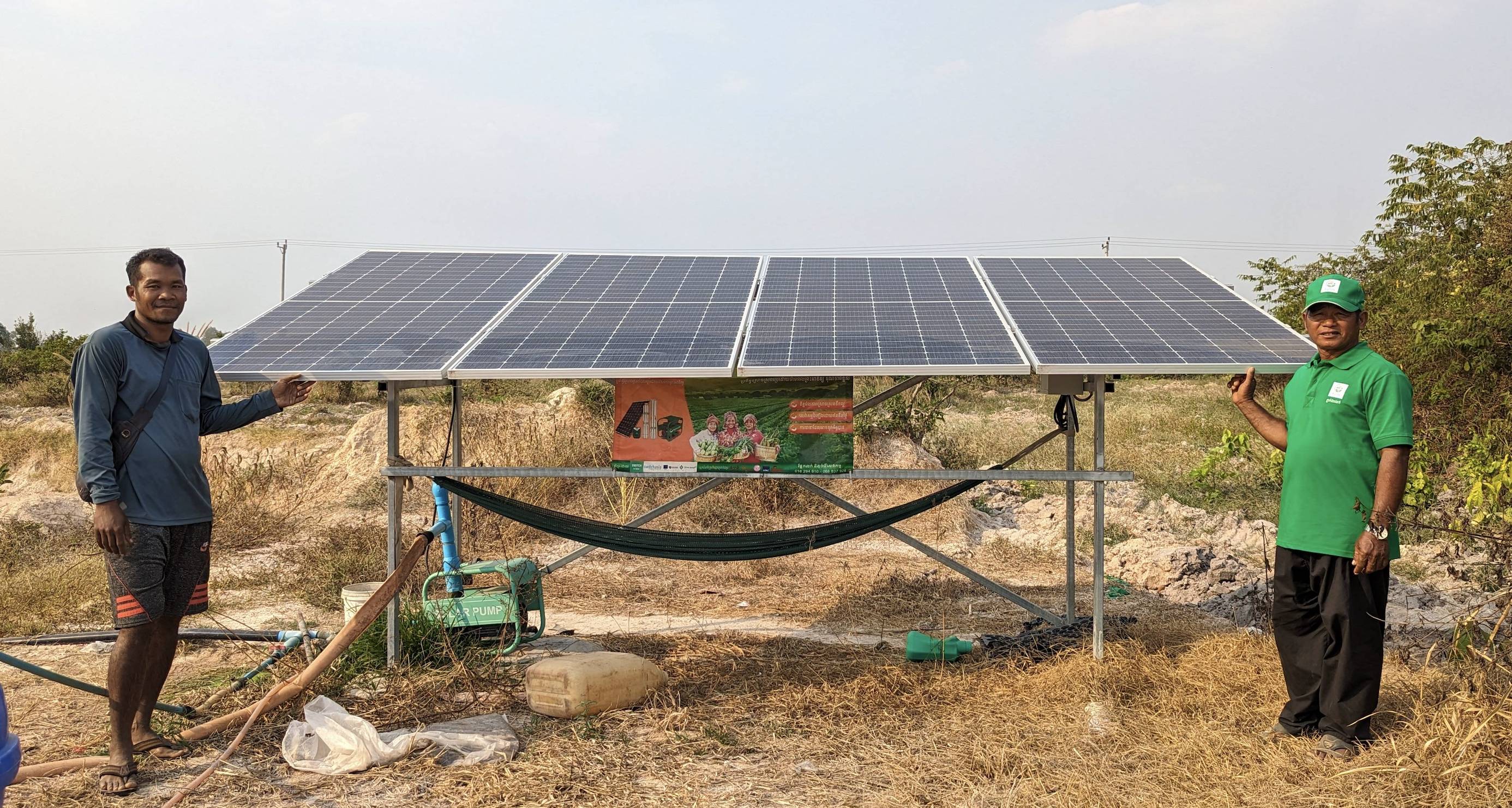
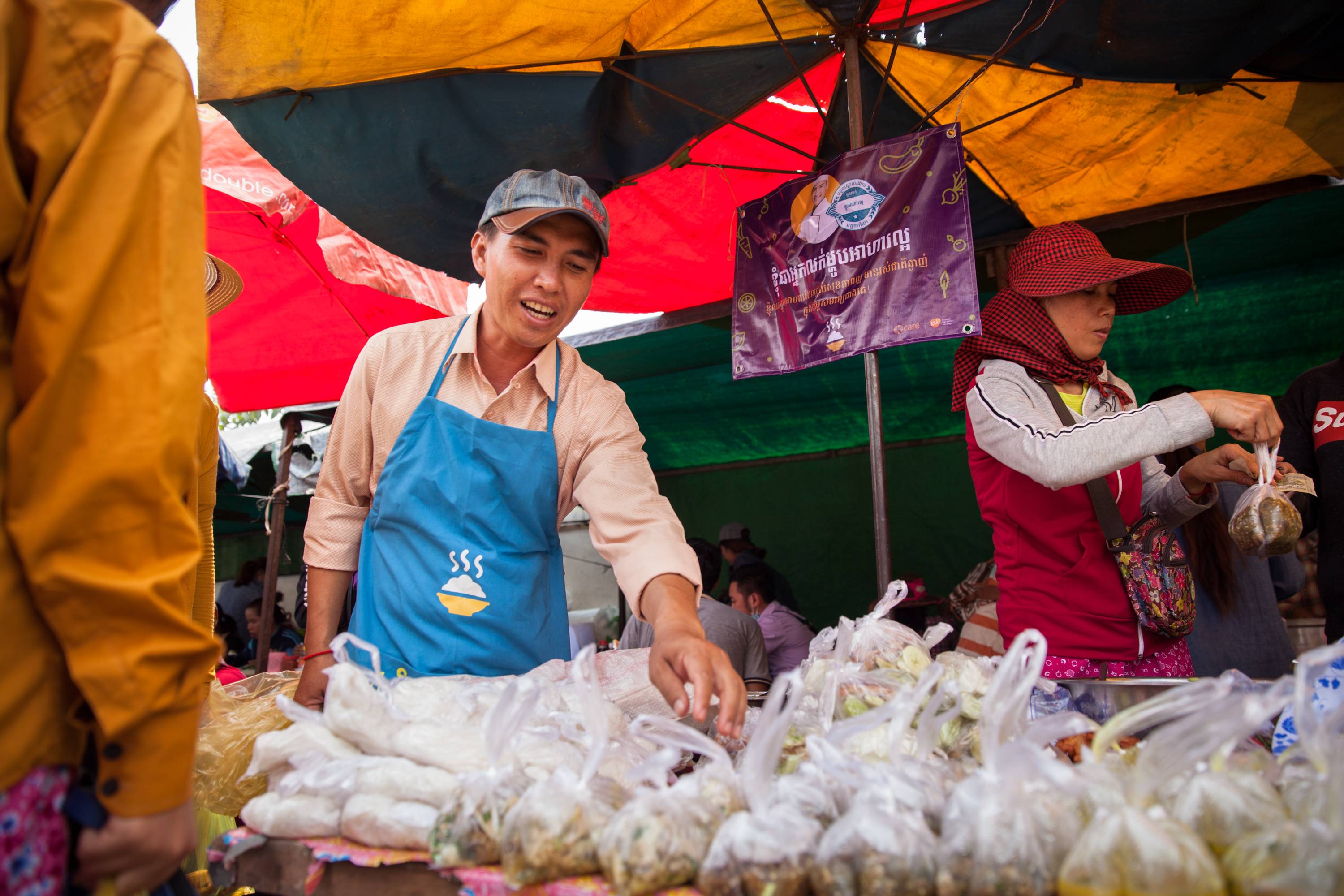
The 2021 SWITCH-Asia SCP Scoping study for Cambodia identifies that the industrial sector in Cambodia provides a significant potential for SCP action, through increasing energy efficiency, renewable energy, water use efficiency and pollution control in factories. Other areas of importance include building construction, eco-tourism and finally green public procurement.
A look back at milestones that shaped our work
2018
SCP Facility
- Preliminary assessment of SCP related policies, activities, needs/gaps, and opportunities.
Regional Policy Advocacy Component (RPAC)
Facilitated the participation of Cambodian key-stakeholders in the following regional/ sub-regional activities:
- Asia Pacific Low Carbon Lifestyles Challenge (19-22 Mar 2018), hosted by Thailand, regional level
- Transforming Asia Pacific: Innovative Solutions, Circular Economy and Low Carbon Lifestyles (17-19 Sep 2018), hosted by Thailand, regional level
- Asian Circular Economy Leadership Academy (3-8 Dec 2018), hosted by Thailand, regional level
2019
SCP Facility
- In December 2019, request for support to formulate Cambodia SCP Roadmap and Demonstration Project was received from the National Focal Point from the National Council for Sustainable Development.
Regional Policy Advocacy Component (RPAC)
Facilitated the participation of Cambodian key-stakeholders in the following regional/ sub-regional activities:
- “Sustainability Reporting – Thinking Circular Economy by Businesses” - This event was organised back-to-back with 2019 Asia Pacific Forum on Sustainable Development (27 Mar 2019), hosted by Thailand, regional level
- Businesses Accelerating Inclusive Green Economies – "Leaving No One Behind” - Side event on the Responsible Business and Human Rights Forum co-organised by the Royal Thai Government, OECD, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), ESCAP, International Labour Organization (ILO) and with the participation of the UN Working Group on Business and Human Rights (11 Jun 2019), hosted by Thailand, regional level
- 2019 Southeast and Northeast Asia Policy Dialogue and Training on “Harmonizing SPP practices and Measuring SPP benefits” - The activity took place in parallel with a series of events related to green procurement organized by the China Environmental United Certification Center (CEC) (23 - 25 Oct 2019), hosted by China, regional level
- WEBINAR: SDG 12.1 Reporting for SWITCH-Asia Countries – Connecting the dots between actions and reporting (5 Nov 2019), regional level
- Policy Dialogue on SDG12 Reporting (21 Nov 2019), hosted by Vietnam, regional level
- 2019 SWITCH-Asia Leadership Academy on Circular Economy (2-6 Dec 2019), hosted by China, regional level
- "Supporting decision making on SCP through training on Sustainable Procurement” - This event was organised back-to-back with International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Green Technology 2019 (11 Dec 2019), hosted by Thailand, regional level
2020-2021
- Led by RPAC together with partners, developed the National SCP Roadmap
Regional Policy Advocacy Component (RPAC)
- The RPAC has provided technical support to Cambodia on development of policy supporting documents i.e Scoping Study on SCP and the National SCP Roadmap to advocate and mainstream SCP into the national development plans.
Facilitated the participation of Cambodian key-stakeholders in the following regional/sub-regional activities:
- SWITCH2Green Meeting - RPAC initiated the discussion and shared the first report in 2020. (Apr 2020)
- Moving The Needle On Climate Change (10 Jun 2020), – The event was co-organised by the UNESCAP as a part of the 2020 Virtual United Nations Responsible Business and Human Right Forum (RBHRF), regional level
- World Environment Day 2020 (5-7 Jun 2020) – A media kit was provided to call for action to promote SCP as a part of the 2020 World Environment Day (WED) celebration, regional level
- Intervention in regional forum: Webinar on Sustainable Lifestyles for Plastics & Packaging Waste Management During a Pandemic COVID-19 (6 Aug 2020), regional level
- SCP in Tourism: Opportunities and Challenges with COVID-19 (8 Oct 2020), regional level
- Innovation and Connectivity through Farm to Fork (13 Nov 2020), regional level
- Sustainable Lifestyles for SCP (19 Nov 2020), hosted by Thailand, regional level
- Support to Steering Committee of SWITCH-Asia (3 Dec 2020) – RPAC provided support for the annual Steering Committee Meeting and proposed 2021 workplan, regional level
- Regional Policy Dialogue on Circular Cities (4 Dec 2020), regional level
- Regional Dialogue Driving Mechanisms for Eco-Design in Asia (9 Dec 2020), regional level
- Leadership Academy on Circular Economy 2020 (14-18 Dec 2020), regional level
- Webinar: Innovations & Startups (16 Dec 2020), regional level
2021
Facilitated the participation of Cambodian key-stakeholders in the following regional/sub-regional activities:
- Contextualising the Circular Economy for Action (4 Feb 2021), regional level
- Virtual Consultation: Mapping SCP in ASEAN Countries (17 March 2021), sub-regional level
- Technology for Circular Economy: A Prologue to the 2021 SWITCH-Asia Leadership Academy (25 March 2021), regional level
- Circular Economy and Sustainable Lifestyles Course (18 May 2021), regional level
- GO4SDGs High level launch in Asia and the Pacific (21 April 2021), regional level
- World Environment Day 2021 (4 June 2021), regional level
2022
SCP Facility
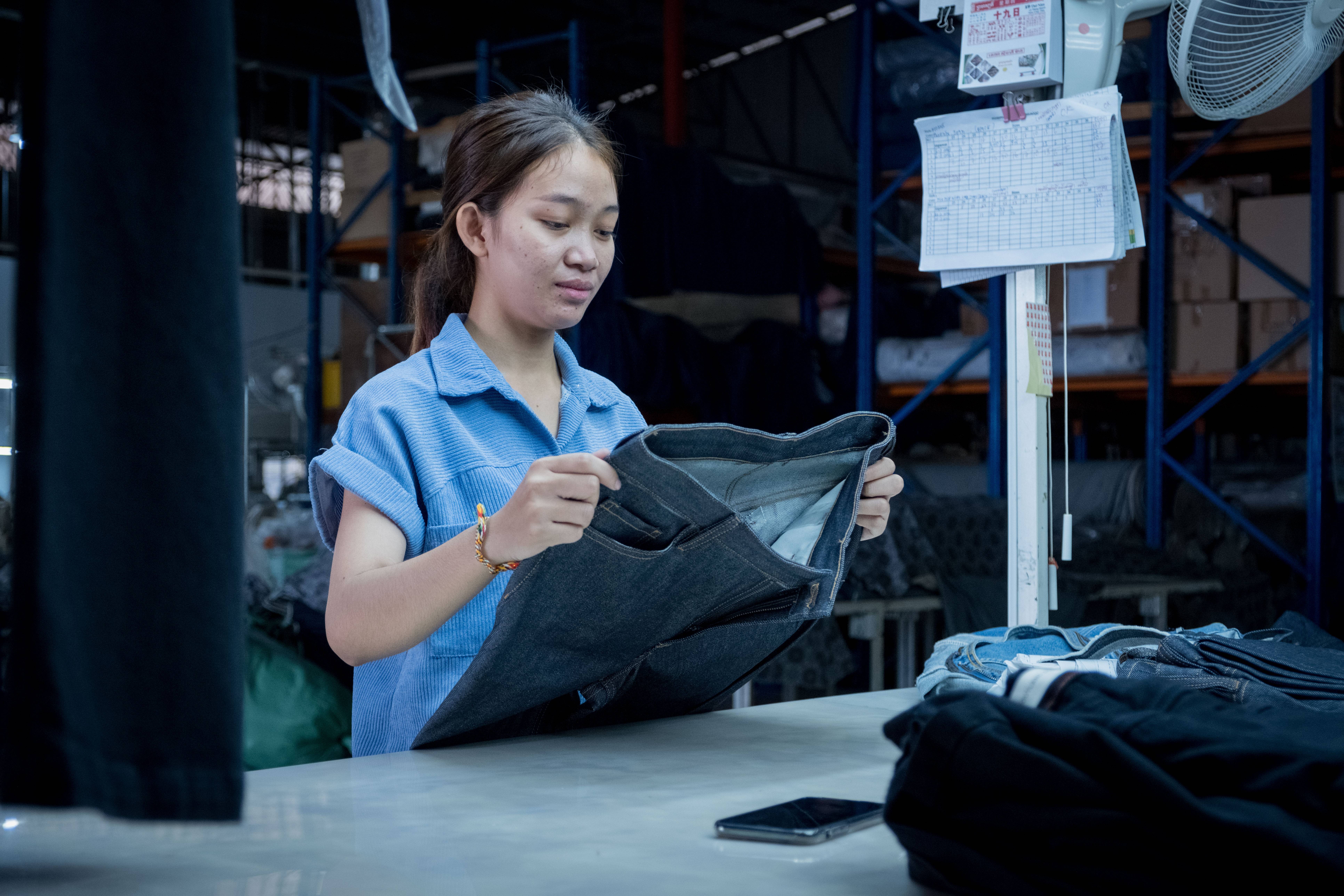
- Led by the SCP Facility, policy analysis report prepared on SCP and circular economy in the garments sector focused on waste reduction, in consultations with stakeholders including collaborations with SWITCH-Asia Grant projects
- Capacity building activities for stakeholders working in the garment and textile sector are being implemented with a focus on the integration of Circular Economy in policy actions and business operations, in line with the National SCP Roadmap and the Policy Analysis Report.