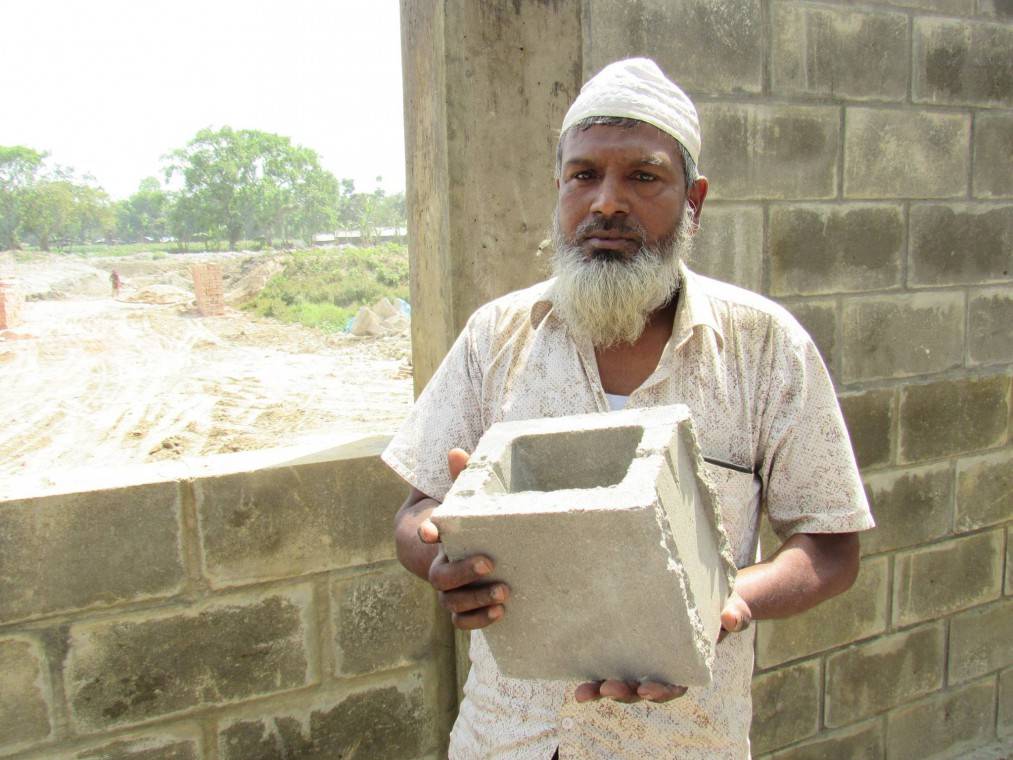
Md Abul Bashar has good reasons to like the alternative bricks and blocks developed by the EU SWITCH-Asia Promoting Sustainable Building in Bangladesh (SusBuild) project. The raw material and production are greener than traditional burned clay bricks. They are made of dredged river sand, stone dust and a small percentage of cement, rather than agricultural top soil, and do not need coal or wood to dry.
The SusBuild project is engaged in contributing to the delivery of what Bangladesh’s capital Dhaka and other urban hubs urgently need: an option to cut air pollution and energy use from traditional brick kilns as well as reduce overall construction costs.
I like the hollow-block; it can be a good alternative to fire-bricks for our construction work, says Md Abul Bashar, beneficiary of the EU SWITCH-Asia ‘SusBuild’ project
As a mason, Md Abul Bashar, benefited from the technology transfer and capacity building activities conducted under the project. He participated in trainings on alternative construction technologies for masons and now has ideas on how to boost the acceptability of the new material: model constructions using alternative bricks.
SusBuild aims at offering environment-friendly and affordable building material to the construction sector market. Targeting manufacturers, the project develops business models to ensure the upscaling of green brick production. When necessary, the project links businesses to financial institutions to avail of initial business support. To stimulate demand for alternative bricks, the project engages with potential house builders, real estate developers and individual homeowners. The acceptability of the new bricks is a pre-condition for market penetration.
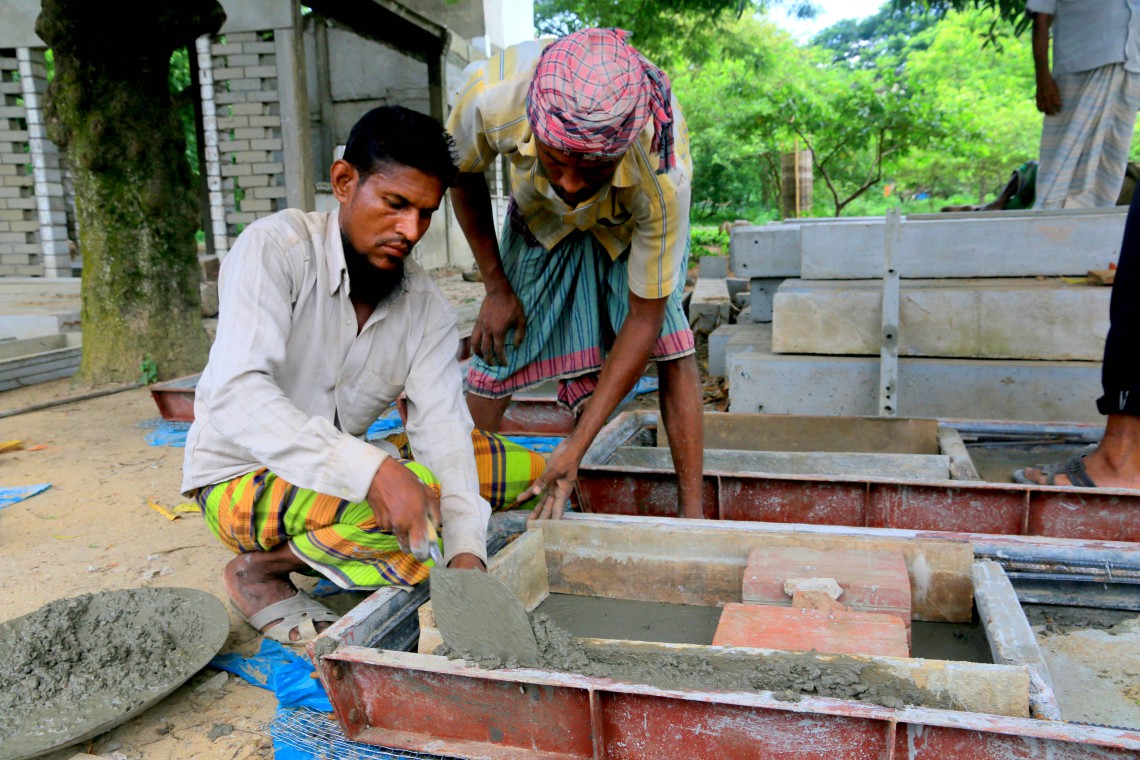

The project targets a wide range of stakeholders, including masons, sub-contractors, civil engineers, architects, urban planners and policymakers. Through the project’s awareness raising activities, judicial experts and policymakers can gain a better understanding of existing policy gaps in both the building code and the brick manufacturing act.
Working closely with the Government, the SWITCH-Asia project is expected to contribute to the implementation of the new Brick Manufacturing and Brick Kiln Establishment (Control) (Amendment) Act, aiming at encouraging the production and use of alternative bricks.
Impacts at a glance
Economic impact
- The project has identified 3 feasible business models for 3 types of Alternative Bricks (ABs)
- New green products in the market: CSEB interlocking, CSEB and Sand Cement Hollow Block
Environmental impact
- 15 targeted MSMEs extracted 10.25% more clay from river basin. This means a reduction in the consumption of topsoil use to produce traditional bricks.
Social impact
- 90% of the population in the target areas has increased awareness regarding the quality, efficiency, and sustainability of alternative green building technologies compared to baseline.
Climate benefits
- 2 MSMEs in targeted local areas are producing ABs with zero CHG gas emissions.
Green finance
- Meeting organised with brick manufactures and different financing agencies to build relationships between and enable the brick field owners to understand the processes to access bank loans for green financing.
- Engagement of financial institutions to improve access to finance for green building materials was also facilitated.
Target group engagement
- Partnership building with 15 MSMEs to start ABs production. 5 MSMEs are in the process of establishing factories to produce ABs. 1 MSME at Jashore has started producing Abs.
- Technical support provided to 15 MSMEs.
- Linkages facilitated among MSMEs, suppliers, and buyers of alternative bricks raw materials.
- 77 interventions with MSMEs on transition to production of green building materials.
- 69 batches of technical training sessions for 2029 technical experts (engineers, architects, urban planners, diploma engineers, students, masons)
Policy development
- The new policy approved by the Government of Bangladesh bans all polluting and hazardous brick production systems, minimising air pollution and improving environmental health.
- Types of policy changes/new regulations contributed to: Definition of Brick and Block, use of ABs in the construction sector, Production of ABs in brick kiln, banned the use of firewood in brick production, Banned the use of topsoil in the brick production, No need for approval and license by the local authority to produce ABs Europe-Asia Cooperation.
Featured on European Commission DG DEVCO website